The Halo-Orbit Insertion (HOI) of the Aditya-L1 solar observatory spacecraft is a significant achievement, showcasing the advanced capabilities of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in handling complex orbital maneuvers. Here’s a breakdown of the key points mentioned in the information:
- Objective of Aditya-L1 Mission:
- Aditya-L1 is an Indian solar observatory located at the Lagrangian point L1.
- Mission objective: Observing and understanding the chromospheric and coronal dynamics of the Sun continuously.
- Halo orbit chosen for optimal observations and minimal fuel consumption.
- Halo Orbit Characteristics:
- Aditya-L1 is in a periodic Halo orbit approximately 1.5 million km from Earth on the Sun-Earth line.
- Orbital period: 177.86 Earth days.
- Advantages of Halo orbit: Smooth Sun-spacecraft velocity change, outside Earth’s magnetosphere, unobstructed continuous observation of the Sun, and constant communication with ground stations.
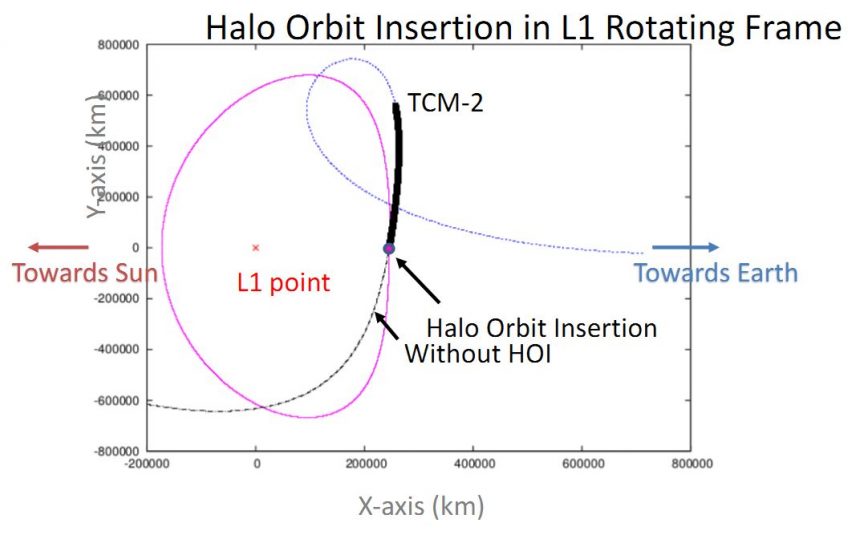
- Halo Orbit Insertion Process:
- Insertion started as the spacecraft crossed the XZ plane in the Sun-Earth-L1 rotating system.
- Essential to nullify X and Z velocity components and achieve the required Y-velocity in the L1 rotating frame for the desired Halo orbit.
- Targeted Halo orbit parameters: Ax – 209200 km, Ay – 663200 km, Az – 120000 km.
- Constant monitoring and adjustment of spacecraft’s speed and position using onboard thrusters.
- Critical Mission Phase:
- Successful insertion indicates ISRO’s capabilities in complex orbital maneuvers.
- Boosts confidence for handling future interplanetary missions.
- Aditya-L1 Journey Overview:
- Launched on September 2, 2023, by PSLV-C57 into an elliptical parking orbit.
- Progressive increase in orbital size using the onboard propulsion system.
- Five liquid engine burns during Earth orbit phase to raise apogee and attain the desired trajectory.
- Trans-L1 injection (TL1I) maneuver executed to reach the target L1 halo orbit.
- Two trajectory correction maneuvers (TCM-1 and TCM-2) conducted to address errors during TL1I phase.
- Cruise phase lasting approximately 110 days to achieve the present condition before HOI on January 6, 2024.
- Payloads and Performance:
- Payloads developed by Indian scientific laboratories (IIA, IUCAA, ISRO).
- Pre-commissioning phase testing confirms satisfactory performance of all payloads.
- Visual Representation:
- The graphical representation illustrates the spacecraft’s movement towards the L1 point, aligning with the Halo Orbit through TCM1 & 2 firings, and the final firing during HOI on January 6, 2024.

The successful execution of the Halo-Orbit Insertion is a testament to ISRO’s engineering prowess and contributes to the ongoing advancements in space exploration and solar observation.